شحن مجاني للأوردرات فوق
1000 ج
رمضان كريم
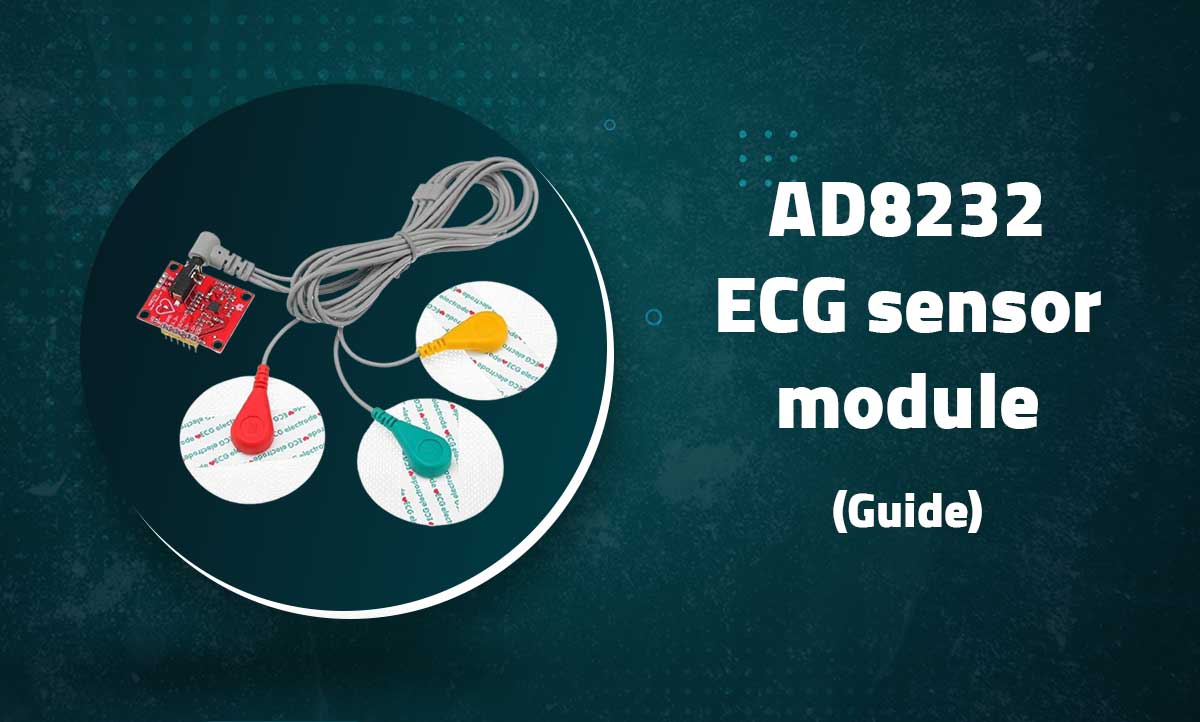
Professional-Grade Biopotential Measurement for Arduino and Medical Applications
The AD8232 ECG Sensor Module is a compact board that measures electrical activity of the heart. This single-lead ECG front end is designed for portable, low-power applications and works perfectly with Arduino for heart rate monitoring projects.
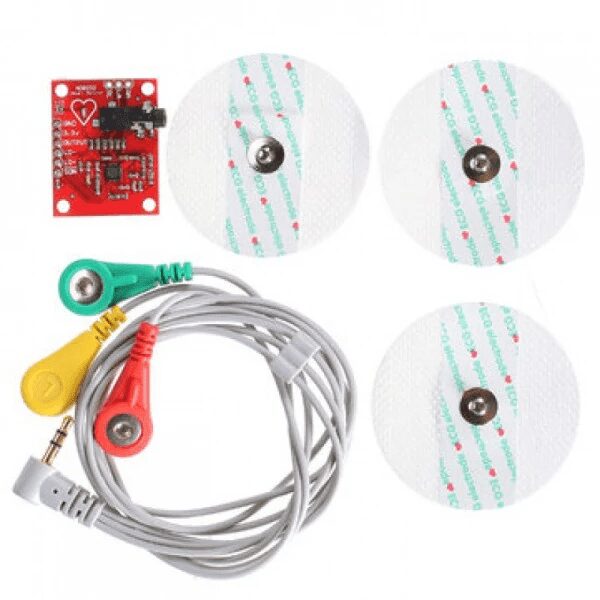

Single-lead ECG monitoring
Integrated signal conditioning
170μA typical current consumption
Built-in electrode contact monitoring
| Input Range | ±1.5mV to ±100mV |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth | 0.5Hz to 40Hz |
| Gain | 100 V/V (adjustable) |
| Supply Voltage | 3.0V to 5.5V |
| Output Type | Analog (ECG signal) + Digital (LO+/LO-) |
| Electrodes | 3x Snap-on (RA, LA, RL) |
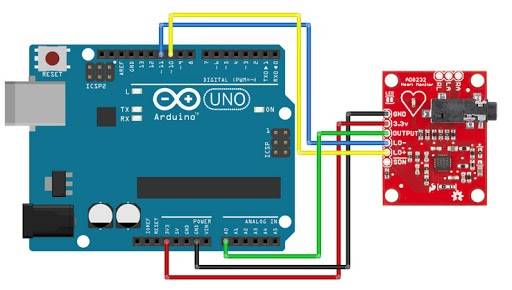
| Pin | Label | Description | Arduino Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3V | Power (3.3V recommended) | 3.3V |
| 2 | GND | Ground | GND |
| 3 | OUTPUT | ECG Analog Output | A0 |
| 4 | LO+ | Lead-Off Detect Positive | D11 (Digital Input) |
| 5 | LO- | Lead-Off Detect Negative | D10(Digital Input) |
| 6 | SDN | Shutdown Control | D4 (Optional) |
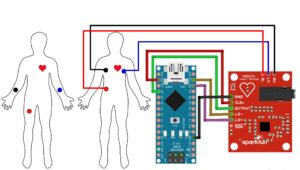
For best results, clean skin and use conductive gel
// AD8232 ECG Basic Monitoring
const int ecgPin = A0;
const int loPlus = 2;
const int loMinus = 3;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(loPlus, INPUT);
pinMode(loMinus, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
if((digitalRead(loPlus) == 1 || (digitalRead(loMinus) == 1)){
Serial.println("Electrode disconnected!");
}
else {
int ecgValue = analogRead(ecgPin);
Serial.println(ecgValue);
}
delay(10);
}
// Detect R-peaks and calculate BPM
unsigned long lastBeat = 0;
float threshold = 520; // Adjust based on signal
float bpm = 0;
if(ecgValue > threshold && millis() > lastBeat + 200){
bpm = 60000 / (millis() - lastBeat);
lastBeat = millis();
Serial.print("BPM: "); Serial.println(bpm);
}// Simple moving average filter
#define FILTER_SIZE 5
int filterBuffer[FILTER_SIZE];
int filterIndex = 0;
int filteredValue = 0;
filterBuffer[filterIndex] = ecgValue;
filterIndex = (filterIndex + 1) % FILTER_SIZE;
for(int i=0; i<FILTER_SIZE; i++){
filteredValue += filterBuffer[i];
}
filteredValue /= FILTER_SIZE;// Log ECG data to SD card
#include
#include
File ecgFile;
void setup(){
SD.begin(4); // CS pin
ecgFile = SD.open("ecg.csv", FILE_WRITE);
}
void loop(){
ecgFile.print(millis());
ecgFile.print(",");
ecgFile.println(ecgValue);
}// Stream ECG via Bluetooth
#include
SoftwareSerial btSerial(10, 11); // RX, TX
void setup(){
btSerial.begin(9600);
}
void loop(){
btSerial.println(ecgValue);
delay(10);
}No account yet?
Create an Account
Recent Comments